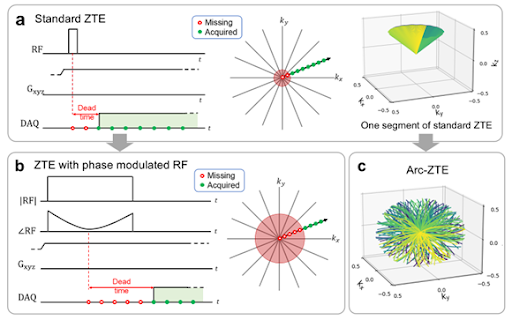
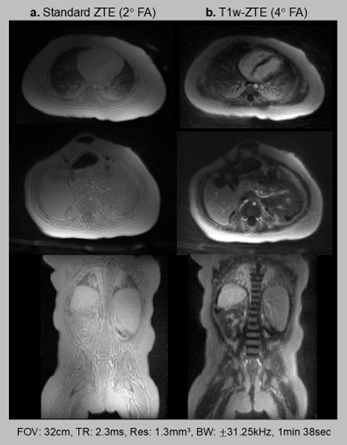
Loud acoustic noise is well-acknowledged as one of the main reasons for patient discomfort in MRI, especially for pediatric patients. For unsedated neonates scanned with the feed-and-swaddle technique, the loud acoustic noise can often wake them up and lead to an unsuccessful exam. Zero echo time (ZTE) imaging (based on RUFIS) enables the unique combination of low acoustic noise and high sampling efficiency, where >99% of each TR can be used for sampling. Our research develops upon standard ZTE to enable (i) quiet T1-weighted imaging and (ii) quiet, dynamic imaging with flexible temporal resolution. We jointly design the quiet acquisition along with an inverse problem-based reconstruction to enable novel applications of quiet MRI in clinical settings.
Key Contributions
- Quiet T1-weighted Imaging: Developed novel acquisition and reconstruction methods to enable T1-weighted imaging with minimal acoustic noise using Zero Echo Time (ZTE) sequences
- Quiet Dynamic Imaging: Extended quiet MRI capabilities to dynamic imaging with flexible temporal resolution, maintaining low acoustic noise throughout the acquisition
- Joint Acquisition-Reconstruction Design: Co-designed quiet acquisition parameters with inverse problem-based reconstruction algorithms to optimize image quality while minimizing noise
People
Last updated: 2025-09-03



